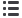
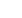
(iv) Sensitivity analysis - interest rate and foreign currency
Interest rate risk
-0.5%
+0.5%
Profit
$’000
Equity
$’000
Profit
$’000
Equity
$’000
30 June 2017
Financial assets
Cash and cash equivalents
(379)
(379)
379
379
Total increase/(decrease) in financial assets
(379)
(379)
379
379
Interest rate risk
-0.5%
+0.5%
Profit
$’000
Equity
$’000
Profit
$’000
Equity
$’000
30 June 2016
Financial assets
Cash and cash equivalents
(376)
(376)
376
376
Total increase/(decrease) in financial assets
(376)
(376)
376
376
This analysis assumes all other variables are constant. All current bonds are issued at fixed rates.
(a) Market risk (continued)
106
NOTE 11
FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT (CONTINUED)
(b) Credit risk
(i) Risk management
The Group’s exposure to credit risk arises from potential default of the counterparty, with
a maximum exposure equal to the carrying amount. Credit risk is managed on a Group basis.
Credit risk arises predominantly from derivatives and trade and other receivables. The Group
does not hold any credit derivatives to offset its credit exposure.
The Group’s Treasury Policy outlines the approach to the management of counterparty credit risk
as approved by the Board. A number of criteria are utilised to manage and spread the level of risk
such as: minimum credit rating of counterparty (investment grade), maximum credit exposure to
any one counterparty and consideration of counterparty concentration risk.
The Group’s policy is that all customers enter into access agreements meeting the terms and
conditions as set out in the agreement before entering the Group’s rail network and receiving
any trade credit facilities.
The Group’s exposure to bad debts has been historically low and statistically insignificant, therefore
no collective loss provision is determined. The Group does have significant concentration of credit
risk associated with major customers providing a high proportion of access revenue, therefore any
bad debt provisions required are assessed on an individual basis.